How to Choose the Right Power Generator for Your Needs: A Comprehensive Guide
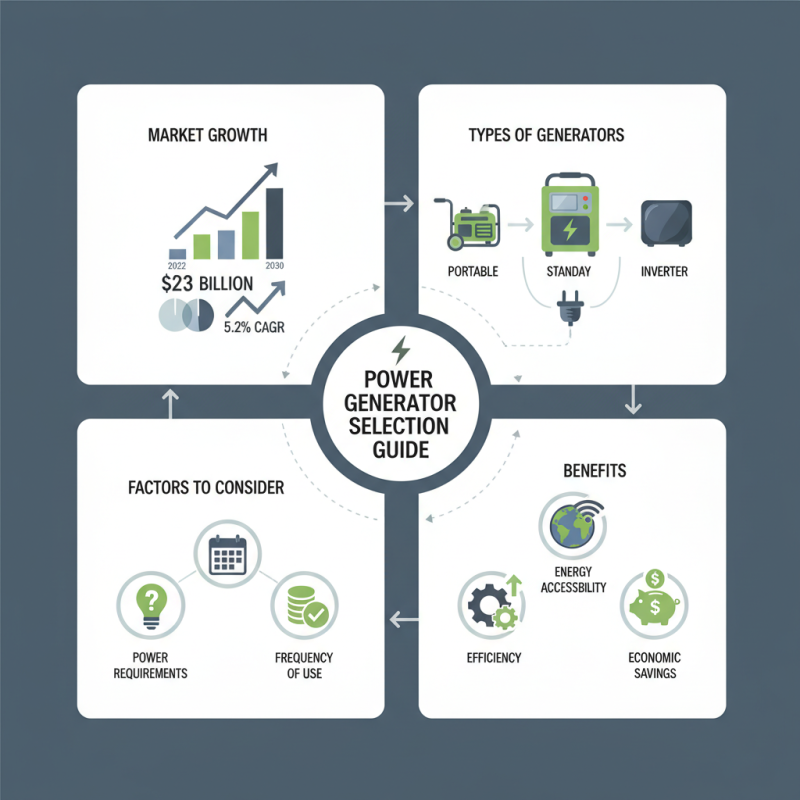
In the modern world, the demand for reliable power sources has skyrocketed, prompting a surge in the market for power generators. According to industry reports, the global power generator market size was valued at approximately $23 billion in 2022, and it is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.2% through 2030. This growth can be attributed to various factors, including the increasing frequency of power outages and a growing reliance on portable power solutions for both residential and commercial use.
Selecting the appropriate power generator for your specific needs requires careful consideration. With a diverse range of products available, understanding the various types of power generators—such as portable, standby, and inverter generators—is essential. Furthermore, a report from the International Generator Association highlights that choosing the right generator not only enhances energy accessibility but also contributes to efficiency and economic savings over time. As such, consumers must evaluate their power requirements, frequency of use, and budget constraints, ensuring they invest in a solution that meets their unique demands while providing the reliability needed in critical situations.
Understanding Your Power Needs and Requirements
When selecting a power generator, understanding your specific power needs is crucial for ensuring that you have adequate energy to meet your requirements. Industry reports, such as the U.S. Energy Information Administration’s Electricity Data Browser, highlight that the average American household uses approximately 877 kWh per month, translating to around 30 kWh daily. It's essential to evaluate the appliances and devices you intend to power during an outage or in off-grid situations. Listing out items like refrigerators, lights, heating systems, and electronics helps create a clear picture of your consumption and aids in selecting a generator with the appropriate wattage.
Additionally, it’s important to consider both starting and running wattage for your appliances. According to industry standards, many appliances require significantly higher starting power to operate than the continuous power they consume during normal use. For instance, a refrigerator may need 1200 watts to start but only requires 200 watts while running. Reports indicate that overestimating your power needs can lead to unnecessary expenses, as generators are often sold based on their maximum output, which may not align with your actual requirements. By carefully assessing your consumption patterns and understanding these power dynamics, you can choose a generator that fits not just your current needs but also allows for possible future expansions.
Power Generator Selection Guide
Types of Power Generators: An Overview
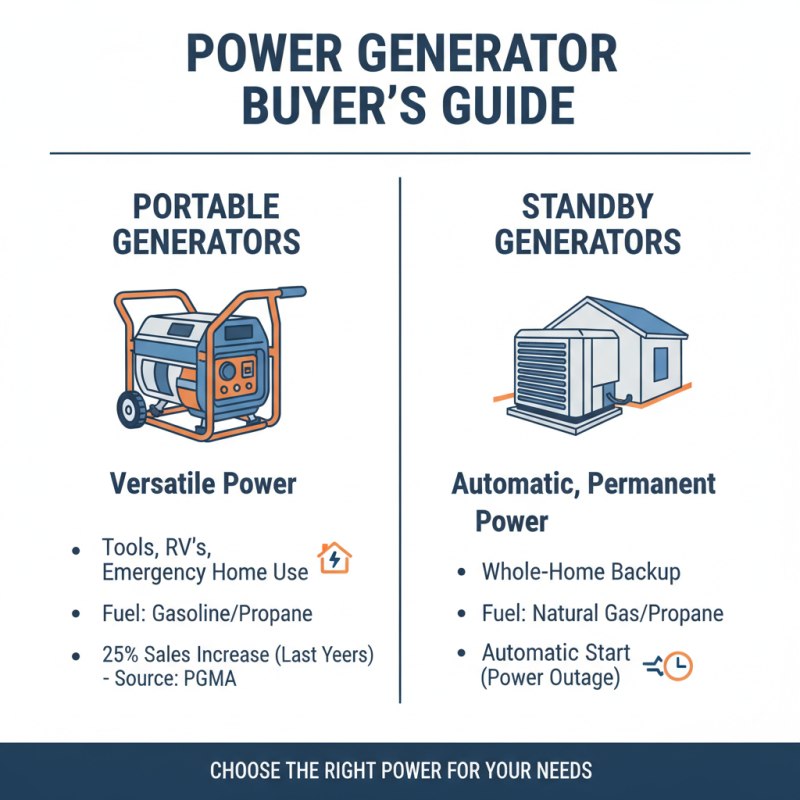
When selecting a power generator, understanding the various types available is crucial. Power generators primarily fall into two categories: portable and standby generators. Portable generators are versatile and can supply power for tools, recreational vehicles, or emergency situations. The Portable Generator Manufacturers Association (PGMA) reports that sales of portable generators have surged, with a rise of over 25% in the past five years, reflecting increased demand particularly in regions prone to power outages. These generators generally run on gasoline or propane and provide power for essential appliances, making them ideal for home use during emergencies.
On the other hand, standby generators are permanently installed and automatically provide power during an outage. According to the National Association of Home Builders (NAHB), nearly 50% of new homes built in hurricane-prone areas include standby generators as part of their essential infrastructure to improve resiliency. These systems usually run on natural gas or propane and are designed to power entire households, making them a reliable option for long-term power needs. Each type of generator serves distinct purposes, making it imperative for users to assess their specific power requirements and environmental conditions before making a decision.
Key Features to Consider When Selecting a Generator
When selecting the right power generator, it’s essential to consider key features that align with your specific needs. First and foremost, assess the power output required for your applications. This involves calculating the wattage needed for all the devices and appliances you intend to use. Generators typically come with two ratings: starting wattage, which is required to start devices with high initial power needs, and running wattage, which is needed to keep them operational. Ensuring that your chosen generator meets these requirements is crucial for optimal performance.
Another essential feature to evaluate is the fuel type. Generators can operate on gasoline, diesel, propane, or natural gas, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Gasoline generators are generally more portable and easier to find fuel for, but they can be less fuel-efficient. Diesel models often provide longer run times and durability but can come at a higher initial cost. Propane and natural gas generators offer cleaner-burning solutions, making them environmentally friendly options but may require additional setup for fuel storage and delivery. Understanding the benefits and constraints of each fuel source will help you select the most suitable generator for your circumstances.
How to Choose the Right Power Generator for Your Needs: A Comprehensive Guide - Key Features to Consider When Selecting a Generator
| Feature | Description | Importance | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Output | Measured in watts, indicates the amount of power the generator can supply. | High | 2500W, 5000W |
| Fuel Type | The type of fuel the generator uses, such as gasoline, diesel, propane, or bi-fuel. | Medium | Gasoline, Propane |
| Portability | Refers to how easy it is to move the generator around. | High | Wheeled or compact designs |
| Runtime | The length of time a generator can run on a full tank of fuel. | High | 8 hours, 12 hours |
| Noise Level | Measured in decibels (dB), indicates how loud the generator operates. | Medium | 50dB, 70dB |
| Start Mechanism | The method of starting the generator, including recoil or electric start. | Medium | Pull-start, Electric-start |
| Safety Features | Include features like overload protection, low-oil shutdown, and circuit breakers. | High | Automatic shutdown, fuel gauge |
Considerations for Fuel Type and Efficiency
When choosing a power generator, one of the most critical considerations is the type of fuel it uses, as this directly impacts efficiency and operating costs. Generators can be powered by a variety of fuels including gasoline, diesel, propane, and natural gas. Each fuel type has its own advantages and disadvantages regarding availability, cost, storage, and environmental impact. For instance, gasoline is readily available and convenient for portable generators, but it can be less efficient and has a shorter shelf life compared to diesel. On the other hand, diesel generators are known for their durability and fuel efficiency, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Additionally, the efficiency of a generator can significantly influence its overall performance and longevity. Understanding the generator's fuel consumption rate and its power output is essential when evaluating efficiency. Generators that convert a higher percentage of fuel into usable electricity are more cost-effective in the long run. Users should also consider the load requirements and how often they will use the generator; a well-sized generator will operate more efficiently, saving both money and fuel over time. Selecting the right fuel type in conjunction with a generator’s efficiency ensures reliable power supply tailored to specific needs, maximizing functionality while minimizing costs.
Budgeting for Your Power Generator Purchase and Maintenance

When budgeting for a power generator, it is essential to consider both the initial purchase price and the ongoing maintenance costs. According to a report from the Generator Manufacturers Association, the average cost of a residential generator can range from $500 to $20,000, depending on the size and features. It's crucial to assess your power needs accurately; for instance, a small portable generator typically provides enough power for essential appliances during an outage, whereas a whole-home generator will require a larger upfront investment.
Additionally, maintenance should not be overlooked in your budget. A study by the National Association of State Energy Officials found that regular maintenance can extend the lifespan of your generator by up to 50%. This typically includes changing the oil, replacing filters, and inspecting components, which can cost around 200 to 400 dollars annually. Investing in a reliable service plan can save money in the long run, as neglecting routine maintenance can lead to more significant repairs and reduced efficiency. Therefore, ensuring a comprehensive budget that accounts for both purchasing and maintenance expenses is critical for maximizing the value and longevity of your power generator.
Related Posts
-

Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Power Generator Service for Your Home Needs
-

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best Home Generators for Your Energy Needs
-

Understanding the Benefits of Using a Generator Service for Your Energy Needs
-

Top 10 Generator Service Providers Transforming Energy Solutions in 2023
-

2025 Top Standby Generator Types: Your Ultimate Buying Guide
-

Understanding the Benefits of House Generators for Emergency Preparedness
