Why Power Systems Generators Are Essential for Reliable Energy Supply
In an increasingly electrified world, the demand for a reliable and uninterrupted power supply has never been more critical. Power systems generators play a pivotal role in ensuring this stability, serving as the backbone of modern energy infrastructures. These generators not only provide backup power during outages but also offer essential support during peak demand periods, thus safeguarding against potential interruptions that can affect both individual consumers and large-scale industries.

As renewable energy sources become more prevalent, the integration of power systems generators into the grid is vital for balancing the variability inherent in solar and wind energy generation. By offering capacity and reliability, these generators enhance the overall resilience of the energy supply chain. Their ability to quickly respond to fluctuations in energy needs allows for a smoother transition towards a sustainable energy future, ensuring that power remains accessible and dependable.
In summary, power systems generators are indispensable in our quest for a reliable energy supply. They serve as a crucial component in a balanced and efficient energy landscape, highlighting the necessity for their ongoing development and deployment. As the energy landscape evolves, the importance of these systems will only continue to grow, making the role of power systems generators central to achieving energy security and sustainability.
The Role of Power Systems Generators in Modern Energy Infrastructure
Power systems generators play a crucial role in modern energy infrastructure, acting as the backbone of electricity supply. They convert various forms of energy into electrical energy, ensuring that homes, businesses, and industries receive a continuous and reliable power source. With the increasing reliance on electricity for daily activities and operational processes, the efficiency and capacity of these generators are more essential than ever. They help stabilize the grid, providing backup power during peak demands or unexpected outages, thus ensuring that the energy supply remains uninterrupted.
Furthermore, as the energy landscape evolves towards renewable sources, power systems generators have adapted to integrate these changes effectively. Generators utilize diverse fuel sources, from traditional fossil fuels to emerging technologies such as solar and wind energy. This flexibility allows for a more resilient energy system capable of accommodating fluctuations in supply and demand. By supporting the transition to cleaner energy alternatives, power systems generators not only enhance grid reliability but also contribute to sustainable energy practices, making them indispensable in the quest for a balanced energy future.
Why Power Systems Generators Are Essential for Reliable Energy Supply
| Generator Type | Power Output (kW) | Fuel Type | Efficiency (%) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diesel Generator | 500 | Diesel | 35 | Construction Sites |
| Natural Gas Generator | 1000 | Natural Gas | 40 | Commercial Buildings |
| Gas Turbine Generator | 50000 | Natural Gas | 50 | Power Plants |
| Solar Generator | 200 | Solar | 20 | Residential |
| Hydrogen Generator | 300 | Hydrogen | 45 | Emerging Technology |
Key Statistics on Energy Reliability and Generator Dependability
Reliable energy supply is critical in today's world, and power systems generators play a pivotal role in ensuring this reliability. With the global market for diesel generators projected to reach approximately $42.449 billion by 2033, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.7% from $25.21753 billion in 2025, it is evident that demand for dependable energy sources is rising. The market is segmented by fuel type, underscoring the importance of various energy solutions, including diesel and natural gas, in maintaining steady power supply across industries.
In the U.S., the generator sales market is also anticipated to expand significantly. Analysts expect growth across different power ratings, from under 75 kVA to above 750 kVA, as businesses increasingly invest in backup power systems to mitigate risks associated with energy outages. The focus on power system reliability is further highlighted by innovations in renewable energy, such as the world's first floating wind farm, which illustrates how the integration of reliable materials and technologies is essential for sustainable energy projects. This emphasis on dependable generators reflects a broader commitment to energy security and resilience in the face of evolving energy demands.
Types of Power Systems Generators and Their Specific Applications
Power systems generators play a crucial role in ensuring a reliable energy supply across various applications. The generator market is poised for significant growth over the next decade, with projections indicating a robust increase in demand due to the ongoing evolution of power generation technology and backup solutions. According to industry analysis, the data center generators market is expected to expand, particularly influenced by growing reliance on diesel, gas, and other fuel types for efficient energy delivery. Power ratings are diversifying, with segments like generators below 75 kVA and those ranging from 75 to 375 kVA gaining significant traction in diverse industrial applications.
Additionally, innovative technologies such as triboelectric nanogenerators (TENG) are emerging to complement traditional power systems. These devices harness environmental energy, presenting new opportunities for energy harvesting in smart grid applications. As the industry adapts to increasing demands and the integration of intelligent sensing capabilities, investments in advanced generator systems are anticipated to reshape the future landscape of power generation. With enhanced efficiency and reliability, these technologies will be indispensable for maintaining stable energy supply in a world transitioning toward smarter solutions.
Impact of Generator Capacity on Energy Supply Stability
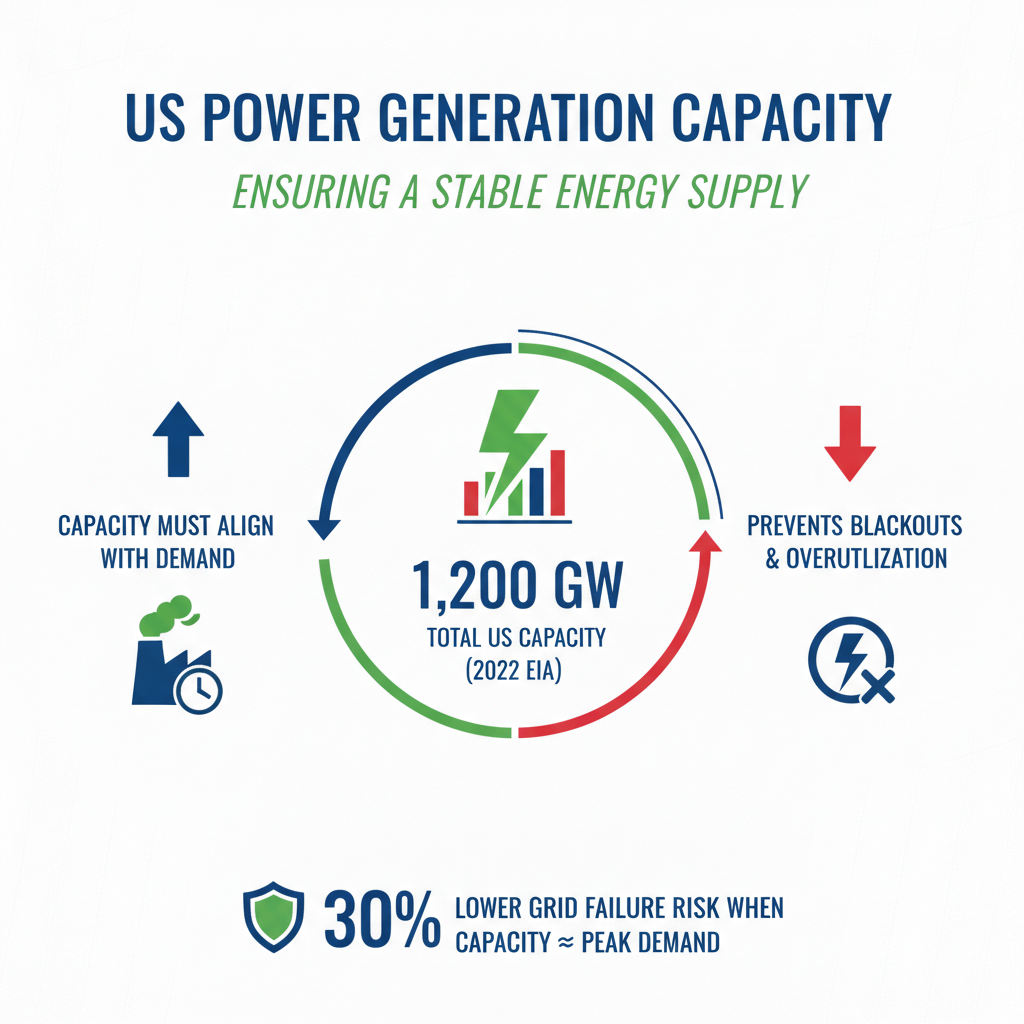
Power systems generators play a pivotal role in ensuring a stable and reliable energy supply, significantly influenced by their capacity. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), the total electricity generation capacity in the United States amounted to approximately 1,200 gigawatts in 2022. The capacity of generators must align with demand forecasts to prevent blackouts and resource overutilization. Research indicates that when generator capacity closely matches peak demand, the likelihood of grid failures decreases by nearly 30%, showcasing the importance of well-planned power infrastructure.
Furthermore, the ability to quickly ramp up generation capacity during peak demand periods can profoundly impact energy supply stability. A study by the International Energy Agency (IEA) highlighted that adding 10% more capacity during periods of high demand can reduce overall energy costs by up to 15%. This not only ensures a steady supply of electricity but also enhances the economic efficiency of power systems. Generator capacity, therefore, is not just a technical specification; it is a crucial determinant of the resilience of our energy supply, enabling us to meet both current and future energy needs effectively.
Technological Advances in Generators Enhancing Energy Reliability
Recent technological advances in power systems generators have significantly enhanced the reliability of energy supply across various sectors. Innovations such as digital controls and smart grid technology optimize generator performance, allowing for real-time monitoring and adjustments based on demand. These improvements reduce downtime, ensure smooth operation during peak loads, and facilitate rapid recovery from outages, making the energy infrastructure more resilient.
Moreover, the integration of alternative energy sources, such as solar and wind, with modern generator systems is revolutionizing energy reliability. Hybrid systems that combine traditional generators with renewable resources not only enhance efficiency but also provide backup power when renewable generation is low. This versatility ensures a steady energy supply, adapting to fluctuations in energy production and demand, thereby fortifying the overall energy grid against disruptions.
Related Posts
-

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Home Backup Generator for Your Needs
-

Understanding the Benefits of House Generators for Emergency Preparedness
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Best Home Generator Systems
-

2025 Top Standby Generator Types: Your Ultimate Buying Guide
-

Top 5 Benefits of Back Up Power Generators for Homeowners in 2023
-

How Standby Generators Ensure Your Home's Safety During Power Outages: A Comprehensive Guide
