Top Small Generators for Home Use and Outdoor Activities?
In today's world, the demand for reliable energy sources continues to grow. Small generators have become increasingly popular among homeowners and outdoor enthusiasts. According to a recent industry report by IBISWorld, the small generator market is expected to reach $4 billion by 2025. This growth is fueled by the need for backup power during outages and for recreational use.
Small generators offer flexibility and convenience. They are lightweight and portable, making them suitable for camping trips or tailgating. Many models are designed to be eco-friendly, using less fuel while providing adequate power. However, users must consider their specific needs. Not all small generators are equal in performance or efficiency.
While small generators offer many benefits, they also present challenges. Noise levels can be an issue, disturbing nearby activities. Moreover, improper use can lead to safety hazards. Reflecting on these factors is essential before making a purchase. Investing in a small generator can greatly enhance outdoor experiences and provide peace of mind at home.

Top Features to Consider When Choosing a Small Generator
When choosing a small generator for home use or outdoor fun, consider power output. Most portable generators offer between 1,000 to 4,000 watts. This output is enough for essential appliances like refrigerators and lights. However, understanding your power needs is critical. Calculate the wattage of devices you want to run simultaneously.
Another key feature is fuel type. Generators typically run on gasoline, propane, or dual fuel. Gasoline generators are more common; they provide high power but require frequent refueling. Propane is cleaner and can be stored longer. Dual-fuel options give you flexibility, but they can be more complex.
Tip: Check the noise level too. Many small generators produce 50-60 decibels. This is the equivalent of a normal conversation. Yet, some units can be annoyingly loud. You may want to consider noise if you use it in residential areas.
Lastly, portability matters. Look for lightweight designs with sturdy handles. Some units weigh over 100 pounds, making them hard to move. Consider the location and how often you'll transport the generator. Balancing these features ensures you make a well-informed choice.
Best Small Generators for Home Use: A Comprehensive Overview
When considering small generators for home use, it’s crucial to know your power needs. Evaluate your essential appliances, like refrigerators and lights. Small generators can provide a backup during outages or for outdoor activities.
Tips: Always check the wattage requirement for your devices. This can prevent overloading the generator. Many people underestimate the power they need, leading to frustration.
Portability is another factor. Choose a generator that is easy to move, especially for outdoor adventures. Weight and size matter, especially if you plan to use it for camping or tailgating. A generator that fits in your car trunk is a must.
Tips: Consider noise levels too. Some small generators are quieter than others. A less noisy option is better for camping trips to respect nature and fellow campers. Remember, not all generators are designed for both home and outdoor use. Make sure you choose wisely.
Ideal Small Generators for Camping and Outdoor Activities
When considering small generators for camping and outdoor activities, portability is key. Many campers want lightweight options. According to a report from the Camping Industry Association, 70% of campers prioritize easy-to-carry gear. Generators can provide energy for cooking, charging devices, or powering lights.
A generator with 1000 watts to 2000 watts is often sufficient for most camping needs. These units can run small appliances without issues. However, noise level is a vital aspect that many overlook. Reports indicate that quiet generators—those operating under 60 decibels—are often preferred by nearly 65% of users. No one wants to spoil the serenity of nature with loud machinery.
Battery life also calls for attention. Many small generators need frequent refueling, requiring careful planning on camping trips. Some users report they need to bring extra fuel or face downtime. It's essential to test how long a generator runs on a single tank, especially in unexpected weather. Outdoor adventure should be seamless, but poor planning can lead to frustration and missed experiences.
Top Small Generators for Home Use and Outdoor Activities
This chart displays the power output of various small generators suitable for home use and outdoor activities, ranging from 1000W to 5000W. Ideal for camping and other outdoor scenarios, the data illustrates how each generator's power output increases with its size.
Comparative Analysis of Fuel Types for Small Generators
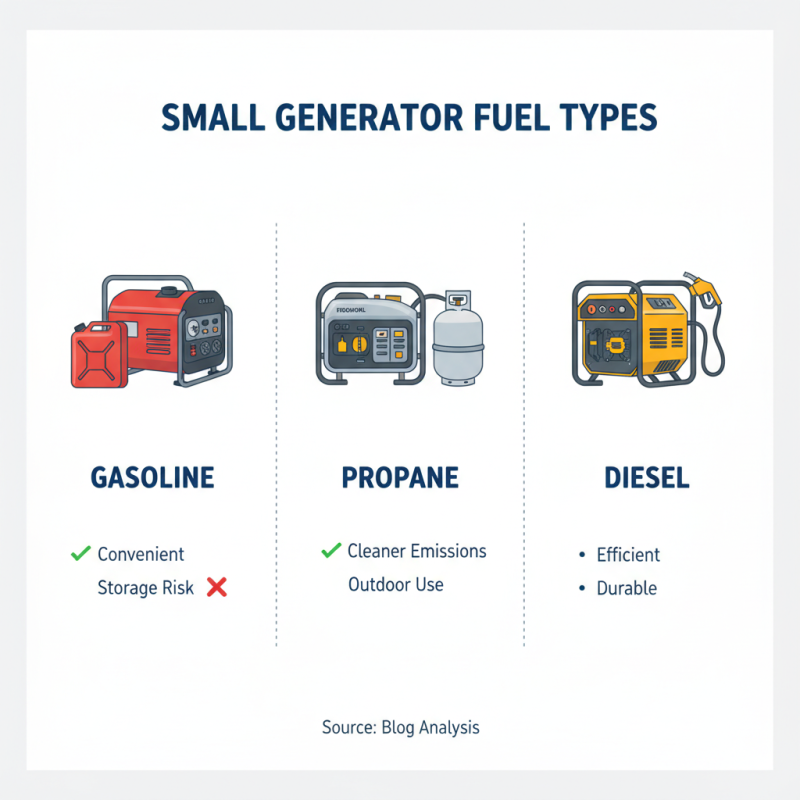
When selecting small generators, fuel type is a critical consideration. An analysis shows that gasoline, propane, and diesel are the most common fuel sources. Gasoline generators are widely favored for their convenience. However, they may present storage risks. Meanwhile, propane generators are often seen as cleaner options. They produce fewer emissions, which is a significant factor for outdoor use.
Interestingly, data from industry reports indicate that diesel generators offer higher efficiency. They typically provide more power output per gallon. However, they come with higher upfront costs. Users sometimes find the noise levels of diesel generators unappealing. This can be a dealbreaker in residential settings, prompting users to reconsider their choice.
Moreover, the environmental impact of each fuel type cannot be ignored. Gasoline contributes to air pollution and greenhouse gases. Propane is cleaner, yet it is not completely free of carbon emissions. Diesel, despite its efficiency, emits particulates that can affect air quality. This conflicting data urges users to reflect on their needs and environmental responsibilities when choosing a generator.
Maintenance Tips to Extend the Life of Your Small Generator

Maintaining your small generator is essential for its longevity. Regular maintenance can prevent breakdowns during crucial moments. Start with the oil. Change it every 50 hours of use. Dirty oil can lead to engine wear. Also, make sure to check the air filter. A clean filter ensures proper airflow. If it’s clogged, consider replacing it.
Fuel management is another key aspect. Use fresh fuel and store it properly. Old fuel can cause starting issues. It can even damage the generator. If your generator sits idle for long periods, use a fuel stabilizer. This helps keep the fuel from degrading. Run your generator at least once a month. This keeps parts lubricated and functioning smoothly.
Pay attention to the battery if your generator has one. Corroded terminals may prevent the generator from starting. Clean them regularly. Inspect the spark plug as well; a dirty spark plug can lead to poor performance. All these steps require minimal effort but are vital for extending your generator’s life. Neglecting even one area can create future problems. Regular check-ups are necessary. They may seem tedious, but they save you time and money in the long run.
Related Posts
-

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best Small Generator for Home and Outdoor Use
-
How to Choose the Best Power Station Generator for Your Needs?
-

Top 10 Tips for Home Generator Installation to Ensure Smooth Operation
-

How Standby Generators Ensure Your Home's Safety During Power Outages: A Comprehensive Guide
-

10 Best Electric Generators for Home Use in 2023: Your Ultimate Guide
-

How to Choose the Right Home Generator Service for Your Needs?
