The Ultimate Guide to Home Generator Systems for Energy Independence
In today's world, the pursuit of energy independence has become increasingly vital for homeowners seeking stability and reliability in their power supply. As natural disasters and unexpected outages become more common, understanding home generator systems has never been more essential. These systems provide an effective solution to ensure that households remain powered during emergencies, allowing families to maintain their daily routines and comfort.
This guide will delve into the various types of home generator systems, their benefits, and critical considerations for choosing the right system to meet your needs. From portable models for occasional use to whole-house generators that can seamlessly integrate into your home’s infrastructure, the options are diverse and cater to varying requirements. By equipping yourself with the knowledge of home generator systems, you can enhance your readiness for any situation, securing peace of mind in an unpredictable world.

Understanding Home Generator Systems: Types and Technologies
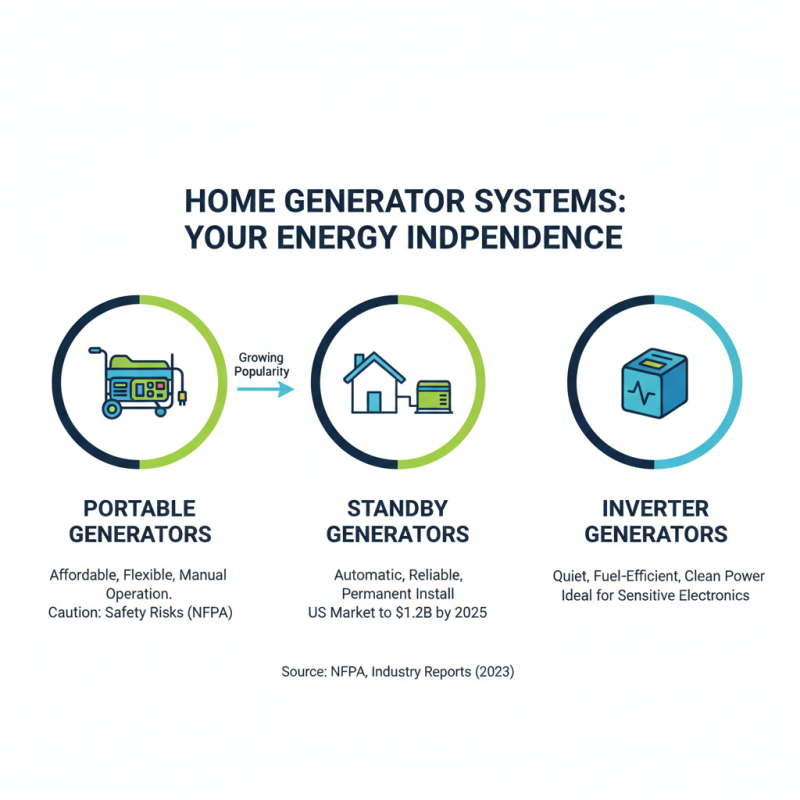
Understanding the various types and technologies of home generator systems is crucial for homeowners seeking energy independence. Home generators typically fall into three main categories: portable generators, standby generators, and inverter generators. According to the National Fire Protection Association, portable generators are the most common choice due to their affordability and flexibility. However, they require manual operation and can pose safety risks if improperly used. Standby generators, which are permanently installed and automatically provide power during outages, are growing in popularity due to their convenience and reliability. The U.S. market for standby generators is projected to reach $1.2 billion by 2025, driven by increasing demand for uninterrupted power supply in residential properties.
Inverter generators offer an innovative solution that utilizes advanced electronics to produce clean, stable power that is safe for sensitive devices. They are often more fuel-efficient than traditional generators and known for their quieter operation, making them suitable for camping or tailgating. Data from industry reports indicate that the inverter generator market is expanding rapidly, with a projected annual growth rate of 8.3% through 2026. As homeowners increasingly turn towards renewable energy sources, the integration of home generator systems with solar power setups is also on the rise, allowing for greater energy autonomy while reducing reliance on the grid. Understanding these technologies enables consumers to make informed choices that align with their energy needs and sustainability goals.
Evaluating Power Needs: Calculating Your Home's Energy Requirements
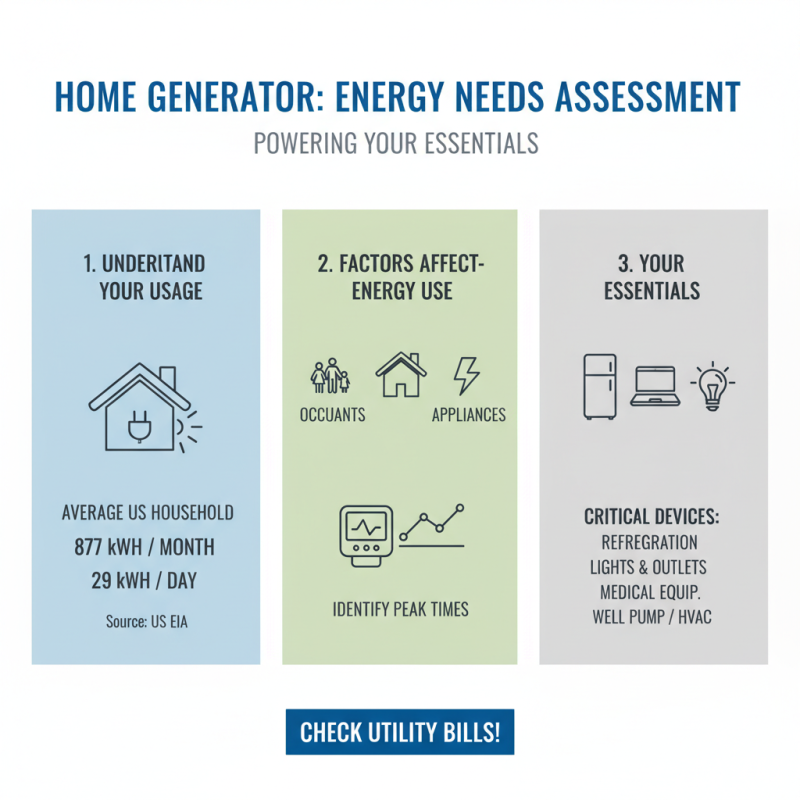
To effectively evaluate your home’s energy needs for a generator system, it’s essential to start with a detailed assessment of your electrical consumption patterns. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA), the average American household uses about 877 kWh per month, which translates to approximately 29 kWh per day. This figure can vary significantly based on factors such as the number of occupants, the size of the home, and the use of energy-intensive appliances. By examining your utility bills, you can identify peak usage times and determine which devices are essential during power outages.
Once you have a clear picture of your energy consumption, calculating the required generator size becomes imperative. A standard approach is to compile a list of priority appliances, including heating and cooling systems, refrigerators, and medical devices that require electricity. For example, a typical refrigerator consumes about 100-800 watts, while central air conditioning units may require between 2,000 to 6,000 watts depending on efficiency and size. By summing the wattages of appliances you wish to power simultaneously during an outage, you can ascertain the minimum generator wattage necessary to meet your home’s energy demands. It is generally recommended to choose a generator with at least 20% more capacity than your total calculated wattage to ensure reliable operation and accommodate unexpected loads.
Key Features of Home Generators: Size, Fuel Types, and Run Times
When considering a home generator system for energy independence, it is crucial to focus on key features such as size, fuel types, and run times. The size of a generator is typically measured in wattage, and selecting the appropriate capacity is vital for meeting your household energy needs. According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, an average American household uses about 877 kWh per month, which translates to about 1,050 watts for essential functions. For whole-house generators, you may need units that can deliver anywhere from 5,000 to 20,000 watts, depending on the appliances you plan to power during an outage.
Fuel type plays an equally important role in the functionality and sustainability of home generator systems. Common fuel options include gasoline, propane, and natural gas, each having its own benefits and drawbacks. A report from the Generac Industrial Power highlights that propane can store energy indefinitely without degrading, making it an attractive option for emergency situations. Additionally, the running time of generators can vary significantly based on fuel type and size. Portable generators typically run for 8 to 12 hours on a single tank of fuel, while standby generators can last for extended periods with a fuel supply like natural gas, which often has an endless supply unless interrupted by a service issue. Therefore, understanding these key features will allow homeowners to make informed decisions, maximizing their energy independence while minimizing risks during power outages.
The Ultimate Guide to Home Generator Systems for Energy Independence
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Size | 3000W to 15000W (estimated power needs for home use) |
| Fuel Types | Gasoline, Diesel, Propane, Natural Gas |
| Run Times | 8 to 24 hours, depending on fuel type and usage |
| Automatic Transfer Switch | Ensures seamless power transfer during outages |
| Noise Level | 50 to 75 dB, varies by model |
| Portability | Standby vs Portable units |
| Cost | $400 to $5000, depending on size and features |
Installation Considerations: Permits, Placement, and Safety Standards
When considering the installation of a home generator system, understanding the necessary permits is a crucial first step. Depending on local regulations, you may need to apply for specific permits before proceeding with the installation. This often includes electrical permits and sometimes building permits to ensure that your generator is compliant with local codes. Failing to obtain the correct approvals can lead to fines or the need to undo completed work, so consulting with local authorities or a licensed contractor is recommended to navigate this process seamlessly.
Placement of the generator is another significant factor to consider for both efficiency and safety. The unit should be installed outdoors in a location that allows for adequate ventilation, minimizing the risk of carbon monoxide buildup. Key considerations include a safe distance from windows, doors, and any combustible materials. Additionally, factors such as noise levels and accessibility for maintenance should guide the site's selection. By choosing an appropriate placement, you can ensure the long-term functionality of the generator while adhering to safety standards and enhancing your home’s overall safety profile.
Maintaining Energy Independence: Cost-Benefit Analysis and ROI of Generators
When evaluating the cost-benefit analysis of home generator systems, it is crucial to assess both financial implications and overall return on investment (ROI). A study conducted by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory indicates that investing in a home generator can reduce dependence on the grid, particularly in areas prone to power outages. Homeowners can expect to save approximately 30% on energy costs during prolonged outages, which can offset the initial investment over time. Moreover, the resilience offered by these systems can prevent losses associated with food spoilage and property damage—a statistic highlighting that power outages can result in an average loss of $250 per household.
Beyond direct savings, the ROI of generator systems can also be measured by their contribution to property value. Research from the Home Improvement Research Institute reveals that homes equipped with backup power systems can see an increase in market value by 5-10%. This increase is particularly relevant in regions susceptible to severe weather events, which are becoming increasingly common due to climate change. By enhancing energy independence and providing a safeguard against fluctuating energy prices and outages, home generators can be a sound financial investment that protects not just the household’s immediate interests but also secures long-term asset appreciation.
Related Posts
-

10 Essential Tips for Choosing the Best Home Generator Systems
-

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Home Backup Generator for Your Needs
-

Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best Home Backup Generators for Your Needs
-

Why You Need a Backup Generator for Home Security and Peace of Mind
-

Essential Tips for Choosing the Right Power Generator Service for Your Home Needs
-

How to Choose the Best Back Up Power Solutions for Your Needs in 2025
